TS.CREATE key [RETENTION retentionSecs] [LABELS field value]Redis TimeSeries
What is a Time Series?
series of data points ordered by time
most commonly sequence taken at successive equally-spaced points in time.
Trend in the last 24 Months
Time Series in Redis
The traditional way:
Sorted Sets & Hashes
Streams
What is missing?
Enhanced queries: Labeling
sensor_id:2, cpu:8, area:5Downsampling (compaction)
Enhanced queries: Aggregation
avg, sum, min, max, range, count, first, last
RedisTimeSeries Basics
Each key is a time series
Each key can have any set of labels
Each key can have multiple downsampling rules
Each downsampling rule will write to a different key
Create a new time series
key: Key name for timeseriesretentionSecs: Maximum age for sampleslabels: set of key-value pairs that represent metadata labels
TS.CREATE ts:2 RETENTION 0 LABELS sensor_id 2 type temperatureAppend a new value to the series
TS.ADD key timestamp valuetimestamp: epoch timestamp (in seconds) or*for automatic timestamp (using the system clock)value: Sample numeric data value (double)
TS.ADD ts:2 1548149181 30
TS.ADD ts:2 * 30Aggregation, Compaction, Downsampling
TS.CREATERULE sourceKey destKey AGGREGATION aggType bucketSizeSecondssourceKey: Key name for source time seriesdestKey: Key name for destination time seriesaggType: Aggregation type:avg, sum, min, max, range, count, first, lastbucketSizeSeconds: Time bucket for aggregation in seconds
Delete Rule
TS.DELETERULE sourceKey destKeyTS.CREATERULE ts:2 ts:avg:2 AGGREGATION avg 60
TS.DELETERULE ts:2 ts:avg:2Downsampling
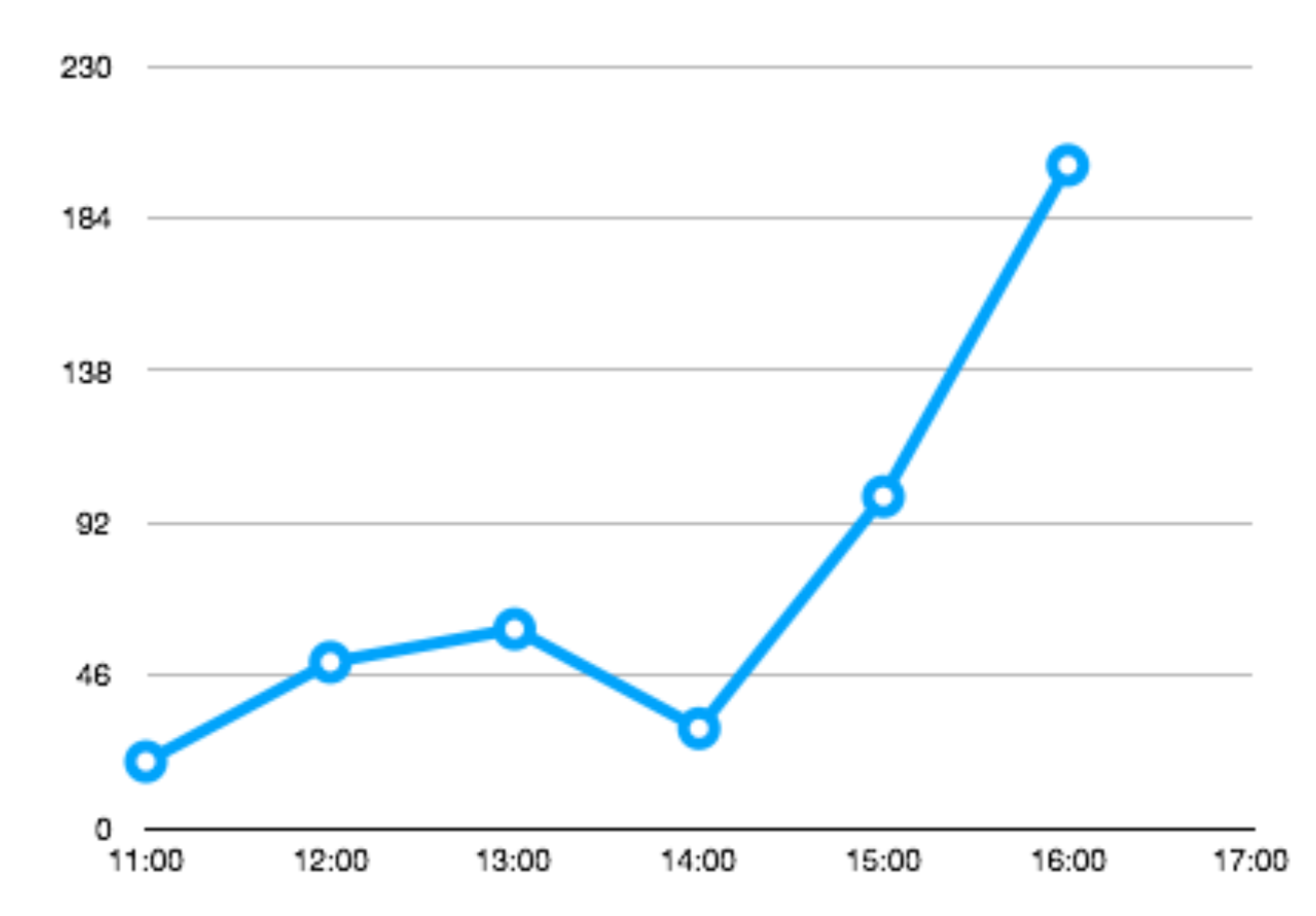
Raw data
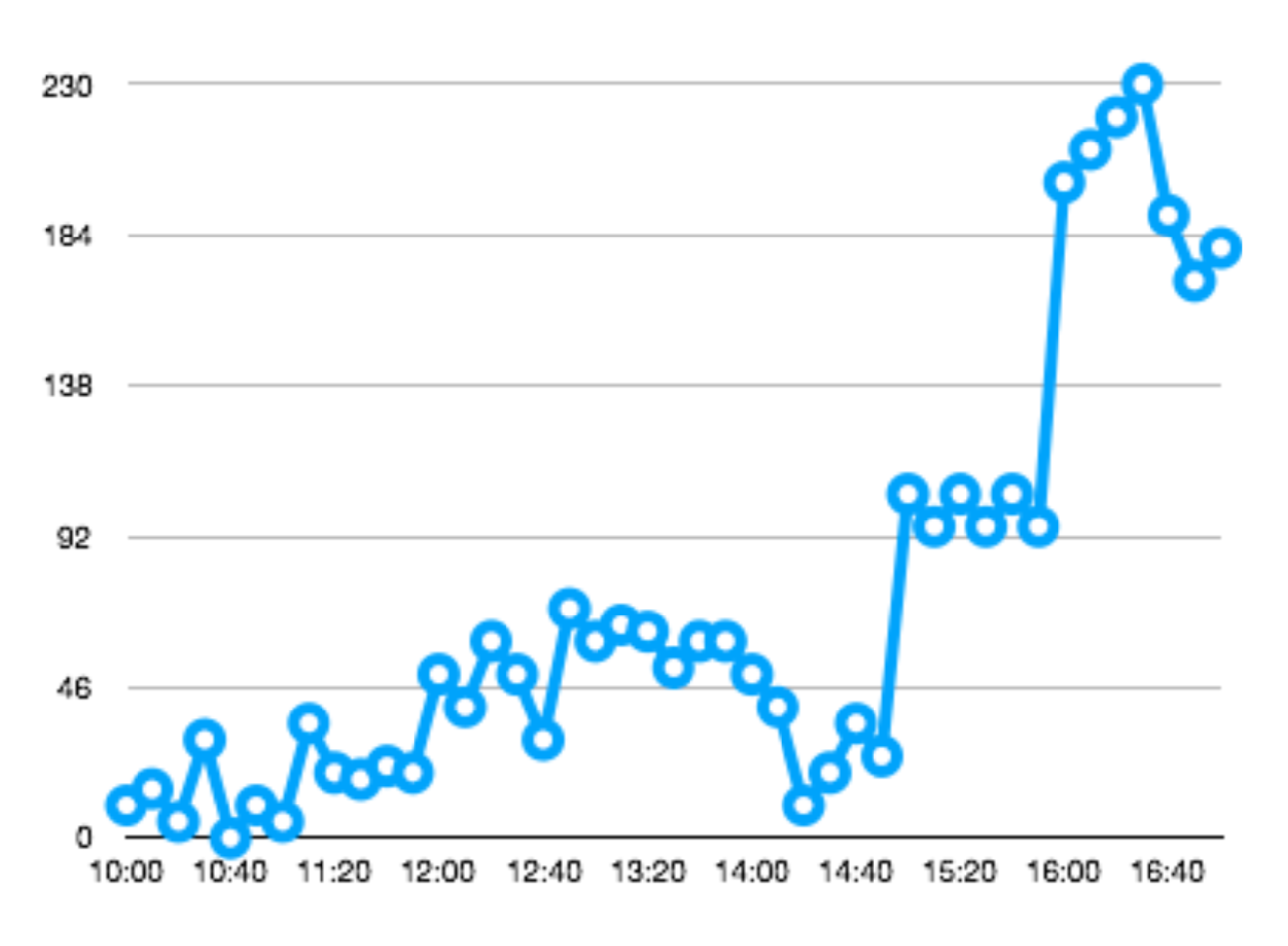
Downsampling
Downsampled and aggregated using average